Social Development Theory
General
Social development theory was introduced in 1920s by Lev Vygotsky, whose theory is according to some the origin of social constructivism1). This theory, sometimes also called cultural-history theory gives a framework for cognitive development in children and argues that the key role in cognition development lies in social interactions. In Vygotsky's own words,
“
every function in the child's cultural development appears twice: first, on the social level, and later, on the individual level; first, between people (interpsychological) and then inside the child (intrapsychological). This applies equally to voluntary attention, to logical memory, and to the formation of concepts. All the higher functions originate as actual relationships between individuals”
2).
What is social development theory?
Vygotsky's initial ideas on education and learning were influenced by Ivan Pavlov and behaviorist stimulus-response learning, yet these ideas later changed resulting in his social development theory. This theory addresses three main themes3):
Social interaction - which according to Vygotsky together with language and culture plays a
crucial role in the process of cognitive development. Opposed to later
Jean Piaget’s
stage theory of cognitive development where development precedes learning, Vygotsky believed that learning precedes development. In Vygotsky's theory mind is not seen as autonomous fromsocial and cultural context. Social interaction here means that a more competent member of the culture will
externalize learned processes which will then be
internalized and thereby learned by a less competent member.
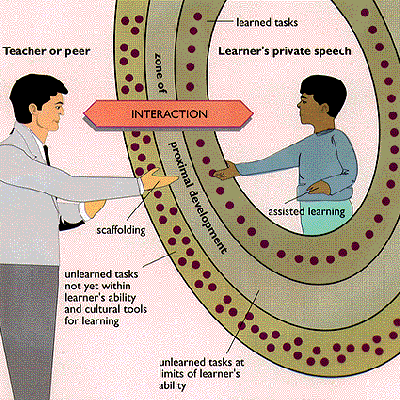
The More Knowledgeable Other (MKO) - a term that addresses a person (typically teacher or instructor, but others as well) or a machine that, when compared to the learner, has more knowledge and skills related to a particular task, process or concept. This person can help a child to learn new concepts and tasks, but only as long as those tasks and concepts don't exceed the zone of proximal development.
The Zone of Proximal Development (ZPD) - a term to describe the zone between learners ability to complete a task with guidance or collaboration and ability to solve it alone. The ZPD is where learning occurs. Motivation for introduction of ZPD lies in observation that children could often accomplish tasks with the help of others that they could not accomplish alone. The zone of proximal development is the difference between a child's current level of development and his or her potential level of development, where full cognitive development is achieved through social interaction. According to Vygotsky, two children may be at the same level of actual development, but given the appropriate help from an adult, one might be able to solve many more problems than the other. This kind of performance was to Vygotsky much more important than performance of a child alone, like the one measured by intelligence tests.
Vygotsky believed that speech and writing are tools developed from the culture in order to mediate social environment. These tools first help children to communicate their needs and later to develop higher order thinking skills. Egocentric speech4) was according to Vygotsky a transition from social speech to internalized thoughts.
What is the practical meaning of social development theory?
First implication of Vygotsky's theory comes from the emphasized importance of social interaction. In accordance with that, interaction, collaboration and peer instruction between learners should be encouraged during the educational process, since it will enhance learning. Teacher should also collaborate with the learners and help them construct meaning and he should also try to encourage externalization:
“
the teacher, working with the school child on a given question, explains, informs, inquires, corrects, and forces the child himself to explain.”
5)
The teacher or any higher-level partner in the educational process should always be aware of the development level of his partner.
Another effective form of teaching is scaffolding - providing learner with help when and as much as needed.
Criticisms
Criticisms of Vygotsky's theory usually emphasize that:
it doesn't take into consideration gender differences,
underestimates abilities and ignores role of an individual,
does not address the issue of how outer world is brifget to internal mind,
valuing performance children accomplish together may result in children
becoming lazy and expecting help even when they can accomplish something on their own.
6)
Keywords and most important names
Bibliography
Zimmerman, Barry J., and Dale H. Schunk. Educational psychology: a century of contributions. Routledge, 2003.
Riddle, E. M. Lev Vygotsky’s social development theory. 1999.
Social Development Theory (Vygotsky) at Learning Theories. Retrieved April 11, 2011.
Logic, Programming, and Robotics
for non-technical students. Constructivism: Constructivist Theory And Social Development Theory. Trinity College, Dublin. Retrieved March 22, 2011.
TIP: Theories. Social Development Theory (L. Vygotsky). Retrieved March 22, 2011.
Read more
Vygotsky, L. S. The Historical Meaning of the Crisis in Psychology: A Methodological Investigation. Plenum Press, 1987.
Vygotsky, L. S. Thinking and Speaking. The M.I.T. Press, 1962.
Newman, Denis, Peg Griffin, and Cole, Michael. The construction zone: working for cognitive change in school. Cambridge University Press, 1989.
Jacobs, G. and Asokan N. Towards a Comprehensive Theory of Social Development. In: Human Choice, World Academy of Art & Science, USA, 1999.
Vygotsky, L.S. Mind in Society: The development of higher psychological processes. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press. 1978.